How To Make Money On Robinhood
Robinhood is one of my favorite apps that I have been using for a while.
I'm very interested in personal finance, and the fact that I can trade without paying commissions on trade makes me extremely happy. If you believe Robinhood is genuine "easy," you are mistaken. Continue reading to learn why!
Today, I decided to dive into Robinhood's revenue model, as well as their past and future plans.
Let's begin by discussing how Robinhood was created.
What is Robinhood?
Robinhood is a finance app that enables commission-free investing in stocks, ETFs, futures, and cryptocurrencies.
It is a FinTech business that enables users to trade stocks, ETFs, futures, and cryptocurrency for free.

Robinhood earns money by providing the services like Robinhood Gold, a margin trading program with a monthly subscription starting at $6, earns interest on customer cash and stocks, and rebates from market makers and trading venues.
Aso, Robinhood generates revenue from order flow charges, subscription fees, interest on stock loans, uninvested funds (by its affiliate banks), and interchange fees.
Robinhood was founded in 2013 and is headquartered in San Francisco, California. It has risen to become one of the most loved FinTech industries. It has raised more than $2.2 billion in financing and has a market capitalization of $11.7 billion. Robinhood is expected to begin trading publicly in 2021.
How Does Robinhood Work?
The users of Robinhood can access the platform using its mobile application.
You can also access your financial information via the Robinhood website, smartphone, and smartwatch apps.
When you sign up for the service, you will receive a complimentary stock. There is a 1 in 150 probability that this incentive will be a high-value stock like Facebook or Amazon.

After providing your personal information and social security number during sign-up, you can fund your Robinhood accounts and immediately begin trading.
The app's versatility and intuitiveness are two of its strongest selling points. After logging in, you can view a summary of your portfolio's results. You can buy and sell on the trading platform with just a few additional clicks.
Robinhood maintains an in-app news stream, as well as a newsletter and podcast (dubbed Robinhood Snacks), to keep its users informed of any significant industry developments.
Additionally, users can build a watchlist to monitor any asset they are considering investing in.
Along with saving, Robinhood provides a cash management service that enables users to gain interest in your account balances. The cash account includes a debit card (issued by Sutton Bank); you can use the debit card to pay for goods and services and withdraw money at over 75,000 ATMs – all of which are fee-free.
The SIPC (up to $500,000) and the FDIC (up to $1.25 million) insure all investment and cash management goods, respectively.
Robinhood's primary value proposition is an investing platform that enables commission-free trading of stocks, exchange-traded funds, options, and cryptocurrencies. As the platform's mission is to democratize the financial system, this is accomplished through three primary components:
- Simple to use.
- Designed for all investors, including newcomers.
- Additionally, it is convenient for experts (even though that is not the primary target).
What is the History of Robinhood?
Vlad Tenev and Baiju Bhatt, who became friends during their studies at Standford, established Robinhood.
Following the 2008 financial crash and the 2011 Occupy Wall Street campaign, many people lost confidence in the financial system. Most of the financial tools and resources were stagged for the rich because of the situation.
Tenev and Bhatt are both first-generation immigrants, descended from Bulgarian and Indian ancestors, respectively. After excelling in high school, the two pursued undergraduate degrees in Mathematics and Physics at Stanford, where they met.
As a result, Tenev and Bhatt were motivated to create a meaningful way for both professionals and first-time investors to be empowered.
The pair clicked immediately and remained friends and roommates during their studies. After graduation, Bhat moved to New York City to work in banking, while Tenev accepted a Ph.D. job at UCLA.
Bhatt invited Tenev to join him in New York City after witnessing firsthand how obsolete and outdated most financial institutions were. They founded their first company in 2009, just a few weeks later.
Celeris was a hedge fund that made investment decisions by algorithmic trading (and the founder's math expertise). Celeris was abandoned two years later, and the founders went on to start their next company.
They founded Chronos Research in January 2011, intending to sell low-latency trading tools to other financial institutions such as banks and hedge funds. Chronos, like its predecessor, was never truly successful.
Robinhood was born out of the founders' observations of several market developments. To begin, people became increasingly adept at managing everything from finances to social contacts via their phones.
Because of the Great Depression, trust in Wall Street (and the financial system in general) was at an all-time low. The Occupy Wall Street movement, which gained momentum in late 2011, exemplified these sentiments.
The top 1% of society were denied access to stocks and other investment opportunities. In the past, incumbents such as ETrade and Charles Schwab charged customers between $7 and $10 for a trade – fees that rendered investing incomprehensible to the average joe.
The duo required funding to get started. As a result, they pitched the Robinhood concept to over 75 investors, who all said no. Additionally, the founders could not launch the app independently due to the extensive capital requirements of starting a brokerage company.
Tenev and Bhatt eventually had their breakthrough moment. They convinced Index Ventures' Tim Draper and Andreessen & Horowitz's Marc Andreessen to invest $3 million in the first startup's seed round (announced in April 2013).
They launched Robinhood in 2013, a commission-free brokerage app designed exclusively for mobile devices. They initially imagined the app as a way for everyone, particularly millennials, to invest in stocks easily.
In early 2014, Robinhood launched its website, inviting users to sign up for the app's waiting list.
A few months later, the iOS application was released in December 2014 (FinTech's Android application in August 2015).
By then, Robinhood's waiting list had grown to over 800,000, making it one of the most anticipated launches in the history of entrepreneurship. Tenev and Bhatt could raise an additional $13 million before the launch due to the growing interest.
Robinhood was finally released to the public, armed with a $16 million war chest. The funding enabled Robinhood to poach top-tier engineers from companies such as Facebook and Uber, which the founders felt was critical to maintaining the app's security.
However, it took over a year for their team to review legislation, obtain approval from the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and join FINRA. The one-year wait and continued work on updates did not disappoint, as it only took them one year to grow their app's waitlist to a million users.
Within a year of its launch, Robinhood surpassed a million users, processed over $1 billion in transactions, raised an additional $50 million in funding, and became the first FinTech company to win Apple's prestigious Design Award.
In 2016, Robinhood launched two critical features that would aid the company in accelerating its growth even further.
They subsequently relaunched their software on Apple smartphones and tablets in 2014 and on Android in 2015.
First, it launched Robinhood Instant, a service that allowed users to borrow nearly $1,000 for trading purposes while their deposit cleared. Additionally, users would be able to trade instantly with any profits earned on stock sales (which normally took a few days to transfer).
However, there was a small catch: users had to join a waitlist to access Instant. The more its user invited their friends, the higher he was moved up in the waitlist. It gave a good boost to the growth of Robinhood as a startup.
The company's second homerun feature is Robinhood Gold, a premium subscription service akin to Netflix.
You can borrow twice the amount of your balance if you have a minimum account balance of $2000 and trade immediately for $10 per month.
Robinhood's business soared to new heights as a result of these two features. In 2016, Robinhood became the fastest brokerage to reach $2 billion in transactions in history.
Robinhood opened its next venture in Australia to expand it internationally fueled with ambition as its first international market. Australians had to pay over $50 for a single trade back then, far exceeding the $7 to $10 fee charged by traditional American brokers. Within days, its waiting list had grown to over 50,000 members in the Australian market.
Also, Robinhood partnered with Chinese Search Giant Baidu after it announced commission-free trading on StockMaster, Baidu's finance app.
The launch lacked explicit regulatory approval, a recurring theme throughout Robinhood's existence (more on that later).
The company's next major milestone occurred in January 2018, when it enabled its customers to trade cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. At the same time, Coinbase was charging its customer around 1.5 to 4% for every cryptocurrency trade.
Additionally, over 100,000 app users frequently searched for cryptocurrency news on Robinhood's app. A survey of its users revealed that 95% would invest in cryptocurrencies.
The launch of its cryptocurrency product exemplified the company's breakneck pace. It took Robinhood and its engineering team less than two months from concept to launch the cryptocurrency product to its user base. With the introduction of cryptocurrency, Robinhood nearly doubled its user base.

When the team decided to launch a banking product (dubbed Robinhood Checking & Savings) in December 2018, they applied the same rigor. Robinhood offered its customers a savings account with a 3% interest rate (the average in the United States at the time was 0.10 percent and 0.08 percent, respectively), as well as SIPC insurance.
However, the issue was that Robinhood's Checking & Savings product was, in fact, a brokerage account extension. Additionally, no one at the SPIC was contacted before the launch (and SPIC CEO Stephen Harbeck stated that Robinhood would never have received their approval).
Some of the startup's product managers expressed reservations about the name being associated with a banking product, to which Robinhood's Bhatt allegedly responded, "fuck it, we're going to do it anyway." He reaffirmed his belief in the name by stating that it would resonate with users.
Just hours after announcing the feature, Robinhood and its leadership faced widespread public backlash. The criticism was exacerbated by the company's employees, who were encouraged to promote the launch on their social media accounts.
Within days, Robinhood deleted all of the information posted and urged all its employees to follow them. The company immediately rebranded the Checking & Savings product as a cash management service.
The cash management product was released in October 2019 after a delay of over ten months.
This time, Robinhood took the time necessary to ensure that everything was set up properly, including offering FDIC insurance through its banking partners (including Goldman Sachs, Citibank, Wells Fargo, HSBC, and more).
By 2019, Robinhood's popularity had spread throughout the online investing industry. Several of the FinTech industry's largest competitors, including Charles Schwab and ETrade, announced permanent fee reductions.
A few key factors fueled Robinhood's meteoric rise to national prominence. To begin, Robinhood was a pioneer in allowing users to trade for free. Second, the app's simplicity made trading extremely easy for new users.
Third, Robinhood's branding is spot on. By positioning the firm as the go-to trading location for the average Joe and associating it with a hero who steals money from the rich and distributes it to the poor, it became accessible to everyone.
Fourth, Robinhood opened up its trading data to the public via an API. This enabled third-party websites such as Robintrack to display data on the most frequently traded securities and investment strategies.
Additionally, the company launched some in-app features that accelerated the social sharing process. For example, it introduced a profile feature that enabled and encouraged users to share their trades publicly.
Fifth, its users became vocal proponents of the app, even participating in forums to brag about their trades. The most notable example is Reddit's wallstreetbets forum, which has grown to over 1.5 million members. Regularly, TikTok videos with the hashtag #robinhoodstocks receive over 8 million views.
These initiatives gained momentum in early 2020 when everyone in the world was forced to quarantine itself. With additional time and government checks available to them, Robinhood users began placing even riskier wagers.
This newly developed appetite for risky bets enabled Robinhood to add another 3 million users to its platform in the first quarter of 2020, adding to its previous revenue, which was already a total of 10 million.
Regrettably, the influx of new users brought its own set of complications. The app experienced three outages for two weeks, locking users out of their accounts and funds – and thus preventing them from cashing out on some of their trades. Many of them were galvanized into filing class-action lawsuits, the outcome of which is still unknown.
What made matters worse was the fact that no one at the company could be contacted for advice. Indeed, Robinhood dismantled its customer service center in 2017 after determining that it was a cost center rather than an asset.
Indeed, Robinhood boasted to investors that the company's lack of physical locations and human capital was a strength. According to a previously leaked pitch deck, Robinhood had 23,700 customers per employee, compared to Charles Schwab's 595.
In some instances, the large number of Robinhood traders appeared to have influenced stock pricing. Hertz, the car rental company that filed for bankruptcy in May 2020 saw its stock price jump 1,462 percent (from $0.40 to $6.25) as a result of thousands of bets placed by Robinhood traders.
As a result, Robinhood decided to disable API access. It was believed that the data available on the websites such as Robintrack inspired many ill-advised trades executed on its platform.
Robinhood responded by assuring users and the general public that the company would invest heavily in making its platform safer and more user-friendly.
This included the release of educational content on options trading and user experience changes, as well as a donation of $250,000 to the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention.
Additionally, the company has committed to working closely with US regulators.
However, even the flood of negative news with a canceled U.K. launch along with a hacking attack against thousands of Robinhood customers. However, these things could not derail Robinhood's growth train.
For example, Robinhood reported that on average, it processed 4.3 million trades per day in June – more than E*Trade and Charles Schwab combined!
Nonetheless, the trading application remained the focal point of attention. In January 2021, Robinhood came under fire for prohibiting users from purchasing GameStop, AMC, and other stocks. Many believed that the hedge funds directed its leadership team to establish the trading halt.
Robinhood raised an additional $3.4 billion in funding to satisfy its collateral obligations and comply with SEC regulations. The SEC regulations required the firm to have a specific amount of cash on balance to cover any default.
However, the damage had already been done. Within hours of the trading halt, Robinhood users filed a class-action lawsuit against the company. Its rating on Google's Play Store plummeted to one, with many users announcing their intention to abandon the platform entirely.
As a result, Robinhood has decided against pursuing an initial public offering (IPO) soon. Rather than that, the firm intends to strengthen its balance sheet and hire financial experts to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
According to Forbes, Robinhood is currently estimated at $12 billion in 2021.
How Robinhood Makes Money?
Robinhood earns money by providing services like Margin Investing, Robinhood Gold (a margin trading service with a monthly fee of $6.), Payment For Orders Flow, and Interest On Cash Transaction Fees.

Let us understand each of these revenue streams in detail below.
Robinhood Gold
In 2016, Robinhood launched Robinhood Gold, a premium subscription service. Among the premium features to which Gold members have access are the following:
- Increased instant deposit amounts
- Unlimited access to in-depth stock research (powered by Morningstar) on over 1,700 companies.
- Level II market data, which enables traders to assess bids and offers for any given stock.
- Margin investing is possible (more on that in the next chapter)
Gold subscriptions begin at $5 per month and go up to $50 per month. Pricing is determined by the amount of money borrowed on margin by traders.
As with any modern subscription service, users can try the service for 30 days for free. Additionally, the service is revocable at any time.
Robinhood's revenue model is based on premium subscriptions. They offer a "Gold Subscription," a premium margin account with monthly fees starting at $10.
Gold Purchasing Power: Robinhood Gold provides up to a twofold increase in purchasing power, allowing you to invest more and access your funds immediately after selling stocks. (For example, if you have $10,000 in cash, you can borrow an additional $10,000 from Robinhood).
Increased Instant Deposit Capacity: Rather than waiting 2-3 days for your bank funds to be transferred to your Robinhood account, Robinhood Gold enables instant access.
Additionally, if you have a premium account with a balance of at least $2000, Robinhood allows you to purchase stocks on margin. What does this imply?
Essentially, Robinhood enables you to borrow money to increase your potential earnings when a stock increases in value. However, if you make a bad bet and the stock price falls, Robinhood may sell the stock on your behalf to repay the loan.
Payment For Orders Flow
When you perform a transaction on (almost) any online trading site, it is routed to a so-called market maker who compensates the platform for deal flow.
Market makers also make superior offers to compete with stock exchanges (like the New York Stock Exchange or NYSE). Robinhood collaborates with various market makers, such as Citadel or Two Sigma, to give consumers the highest possible purchase price.

The market maker's objective then becomes to benefit from the bid-ask spread (or turn), which is the difference between the quoted prices for immediate selling (bid) and an immediate purchase (ask) (ask).
As a result, it becomes a company of arbitrage. The market maker executes trades algorithmically (without human intervention), allowing for the execution of thousands of trades simultaneously.
Historically, the practice of selling to market makers has drawn broad condemnation from consumer advocacy organizations and financial regulators alike. To begin, the process itself often lacks clarity as a result of its automated execution.
To that end, the Wall Street Journal reports that the SEC has been investigating Robinhood for failing to adequately disclose its practice of selling user orders to high-frequency traders. If FinTech refuses to settle, the investigation will result in a $10 million fine.
Second, due to the practice's lightning-fast execution (milliseconds), it may result in large market fluctuations, often favoring institutional investors rather than the small retail investors served by Robinhood.
Third, the practice can (!) hurt retail investors by preventing them from receiving optimal execution. For example, the market maker can quote a stock at $10 (bid) and then sell it for $20.1 later (ask). As a result, the retail investor forfeits some profits.
Robinhood decided in December 2020 to pay a $65 million fine to the Securities and Exchange Commission for allegedly deceiving its customers (without admitting any wrongdoing). According to the SEC, the order flow payments were made at a lower rate than other brokerage firms. Additionally, it reported that Robinhood failed to reveal how it earns revenue from order flow payments between 2015 and 2018.
On the other hand, this method is essentially what enables commission-free trading on Robinhood. Not long ago, existing brokerages such as E*Trade and Charles Schwab charged customers up to 10% in trade commissions, which far outweighs the spread a trader will lose on the order flow.
Recent legislation requires online brokerages to report the revenue they earn from order flow payments. In the first and second quarters of 2020, Robinhood produced $90 million and $180 million, respectively.
Interest On Cash
Robinhood earns income from uninvested cash through its Securities division. The company lends the cash on hand to other banks and earns interest on the loans.
Robinhood pays interest on available cash deposits in your account, close to how banks do.

For example, if you have $500 in your Robinhood account and the interest rate is 2%, they will earn $10 a year on your money.
It's not much, but when multiplied by the 5 million accounts they currently hold, it equates to a sizable amount of earnings.
Robinhood then distributes a portion of those profits back to its customers (after deducting their share), allowing FinTech to pay its users interest (APY on balance).
Robinhood Securities earns interest on cash that is not swept into the Cash Management network of program banks, mainly by depositing it in interest-bearing bank accounts.
Margin Investing
Margin investing enables Robinhood users to borrow funds from the corporation to buy stocks. Robinhood earns money by charging interest on these loans. Users pay a 5% annual interest rate for any margin above $1,000.
Robinhood uses the trader's account balance as a reference for the sum that can be borrowed. This enables the business to measure the probability of payment default more accurately.
If a trader's portfolio value falls below a predetermined level, he or she will earn a so-called margin call. In that case, the trader must either replenish the account with new funds or sell shares (and other holdings) to meet the necessary minimum balance.
Robinhood has previously faced criticism for encouraging users to trade on margin. Due to its largely young user base (the average Robinhood trader is 30 years old), combined with historical market volatility, it may expose (particularly inexperienced) traders to risk they are not prepared to take.
Interchange Fees
Robinhood partners with Sutton Bank to sell a Mastercard debit card. When a customer pays with a debit card, the dealer is paid an exchange fee.
Sutton Bank, which issues the Robinhood debit card under license from Mastercard® International Incorporated, earns an interchange fee from Robinhood Financial, our distributing broker.
The interchange fee is usually between 0.1 and 1%, depending on the country and method of payment (credit vs. debit vs. prepaid).
Many debit and credit card issuers collect interchange fees, which cover transaction processing and fraud loss. The Robinhood debit card is only available in conjunction with a brokerage account offered by Robinhood Financial LLC, a SIPC and FINRA member.
The interchange fee revenue is divided between the card issuer (in this case, Mastercard), the licensing bank (in this case, Sutton Bank), and Robinhood.
Program banks also compensate Robinhood Securities and Robinhood Financial for the funds they sweep.
Other FinTech firms, such as Chime or Revolut, generate revenue through joint ventures with other banks.
Other
Also, Robinhood earns revenue from various other, smaller revenue sources, including revenue from proxy services and fees specified on the Robinhood Financial Fee Schedule.
What was the Total Funding of Robinhood?
Robinhood closed its Series E round of funding in July 2019, raising $323 million at a valuation of $7.6 billion.
Robinhood announced a $280 million Series F funding round in May 2020, valuing the company at $8.3 billion.
It raised $660 million in a Series G funding round in September 2020, valuing the firm at $11.7 billion.
On February 1, 2021, Robinhood reported an additional $3.4 billion in funding led by Ribbit Capital, ICONIQ Capital, Andreessen Horowitz, Sequoia, Index Ventures, and NEA.
The business has raised a total of $5.6 billion in the capital.
What is the Total Valuation of Robinhood?
According to reports, Robinhood was estimated at $12 billion in September 2020, growing to about $20 billion by the end of the year and then doubling to $40 billion in May 2021 in the secondary market.

Is Robinhood Making Money?
Robinhood has invested heavily to expand, but the question remains: is Robinhood profitable?
The Robinhood business model is quite interesting to be profitable, attracting major companies such as Venture Capital to invest significant amounts of money in them. Additionally, they have attracted many millennial investors due to their ease of use and willingness to exchange stocks for free.
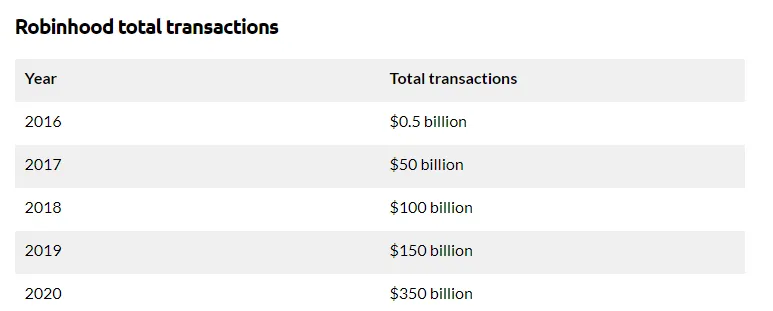
Robinhood earned $673 million in 2020, according to this site.
The business has more than doubled its customer base last year, surpassing E-5 trade's million brokerage accounts.
In February of this year, it released its cryptocurrency trading platform for bitcoin, attracting many new users' attention. They exceeded $150 billion in trade volume in 2018.
While it may seem that the business earns little by charging nothing for each trade, they have successfully leveraged their monetization strategies to develop and evolve into the large company they are today.
What is the Revenue of Robinhood?
In 2020, Robinhood produced $682 million in revenue from payment-for-order flow, a 514 percent rise year over year. It added $3.4 billion to its balance sheet even during the GameStop stock crunch the following year, after temporarily halting trading for a week.

Robinhood announced in May 2020 that it had 13 million active users (NYT). The figure is expected to have risen to 20 million. It was recently listed at $20 billion before its initial public offering, while secondary shares place its valuation at $40 billion.
Does Robinhood Sell its User Data?
As reported previously, Robinhood gets reimbursed for order flow, but it also appears as if the business sells their customers' orders and earns significantly more than their rivals.
This creates a conflict of interest and is detrimental to you as a consumer. The companies to which Robinhood sells your data, such as Two Sigma, Citadel, or Wolverine Securities, have a history of violating securities laws and regulations.
The Securities and Exchange Commission needs all brokerage firms that sell order flows to report who they sell them to and how much they charge.
However, there have been speculations that the disclosures being published are materially different. According to others, something must be going on behind the Robinhood scenes that are being kept hidden from the public.
Also, read, How Does Zoom Make Money?
Final Thoughts About Robinhood
Robinhood, in my view, is one of the most creative and revolutionary financial apps available.
With their latest offensive against Coinbase and the banking system in general, I'm sure they'll win a large number of deals from the market's largest firms. I see Robinhood becoming one of the leading full-service financial services companies in a few years.
Also, check How Does Honey Make Money?
How To Make Money On Robinhood
Source: https://seoaves.com/how-does-robinhood-make-money-robinhood-business-model/
Posted by: colewitis1985.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Make Money On Robinhood"
Post a Comment